Deploy an App Designer Simulation with Simulink Compiler
This example walks you through the workflow of creating a simulation app in App Designer and using Simulink® Compiler™ to deploy it. The example explains the code that is used to build the app.
To open the example, type the following in the MATLAB® command window, or click the View MATLAB Code button.
openExample('simulinkcompiler/DeployingASimulationAppUsingSimulinkCompilerExample')Deploying a Simulation App with Simulink Compiler
In this example, we use an app that is prepared in the App Designer and deploy it with Simulink® Compiler™.
Open and Explore Model
In this example, we use the model of a mass spring damper system. The mass-spring-damper model consists of discrete mass nodes distributed throughout an object and interconnected via a network of springs and dampers. This model is well-suited for modeling object with complex material properties such as non-linearity and elasticity. In this example we use the mass spring damper system. The system is parameterized by mass (m), spring stiffness (k), damping (b) and the initial position (x0). The input to the system is the applied force.
To explore this model with different values of the tunable parameters, create the following model workspace variables:
Mass - m.
Spring stiffness - k.
Damping - b.
Initial position - x0.
open_system('MassSpringDamperModel');

Create the App in App Designer
Use the MATLAB App Designer to create an app to simulate the model with different parameter values and input signals. To learn more about how to create an app using the App Designer, see Create and Run a Simple App Using App Designer Use the MassSpringDamperApp.mlapp file to use the app.
MassSpringDamperApp
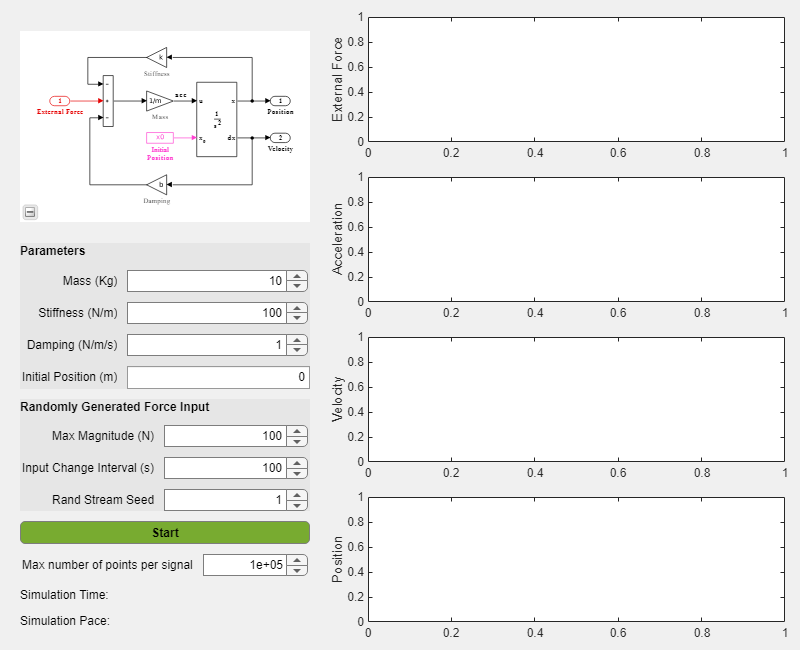
App Details
The main part for the app is the simulate button callback function. It has the following salient parts: setup the SimulationInput object, configure it for deployment, simulate, and plot the simulation results.
The functionality of the application to change and experiment with the tunable parameters is defined in the callback function SimulateButtonPushed. This callback function enables you to change, experiment and analyze different simulations by modifying the values in the app designer.
Callback Functions
This section explains the code written to create the app, MassSpringDamperApp. The code for the MassSpringDamperApp uses many callback functions. You can inspect the code by opening the MassSpringDamperApp,mlapp file in the App Designer. The createSimulationInput and modifyParameterDuringSim functions help set the values while also updating the simulation values in the app. We use the Simulink.SimulationInput object to set the variables to the model and use these variables to change the values and analyze the model.
Create the Simulink.SimulationInput Object in the createSimulationInput Function
In the following function, create a SimulationInput object, SimInp for the model MassSpringDamperModel. Use the setVariable method on the SimulationInput object to load the parameter values into the variables k, m, b, and x0. Now that we have assigned all the values to the variables and set the input signal, the Simulink.SimulationInput object is required to be configured for deployment. Use the simulink.compiler.configureForDeployment function of Simulink Compiler. This function handles all the settings required for the script to be compatible for deployment by setting the simulation mode to rapid accelerator, and by setting the parameter RapidAcceleratorUpToDateCheck to off.

Modify Parameters During Simulation
To allow modification of the parameters during the simulation, use the function |modifyParameterDuringSim|. This function gets the current simulation stats and then if the simulation is running or paused, enables you to modify the values for the simulation.

Simulate and Plot the Results
Use the configured Simulink.SimulationInput object to run the simulation with the designed app. The addPoints function plots and traces the simulation results as the app is running.

Test Out the Application in App Designer
Before deploying the application, ensure that the app runs in the App Designer. Click the Simulate button on the app to verify that the application works by simulating the model for different values.
Compile Script for Deployment
To compile the app, use the mcc command, followed by the script name.
mcc -m MassSpringDamperApp.mlapp
External Websites
Running the Deployed Application
Install MATLAB Runtime and Package the Deployable
To run the deployed executable, you need an appropriate runtime environment. For more information, see MATLAB Runtime.
Ensure that the path environment variable is free of other instances of MATLAB Runtime from previous installs. If there are any, remove them.
To install MATLAB Runtime, follow the instructions on Install and Configure MATLAB Runtime.
Compile the deployable for the first time as follows:
Enter
deploytoolcommand in the MATLAB Command Window and select Application Compiler.In the Main File section, add the file to be deployed,
MassSpringDamperApp.mlappIn the Packaging Options section on the toolstrip, select Runtime included in package and enter the
deployed_installerin the text box.Click Package in the Package section of the toolstrip.
Once the package is ready, use the
deployed_installerin thefor_redistributionfolder to install the proper runtime environment for running the deployed application.
Run the Deployed Application
You can run the deployed script only on the platform that the deployed script was developed on.
It is recommended to run the deployed application from the Windows® Command Prompt. Running the deployed application from the command prompt also enables the script to print errors when something is wrong in the deployed application. These errors can help troubleshoot the problem.
Note
The MassSpringDamperApp.mlapp contains
errordlg, and errordlg is not supported on Web
Apps.
See Also
simulink.compiler.configureForDeployment | mcc | deploytool | Simulink.SimulationInput
