What Is Data Preprocessing?
Data preprocessing is the task of cleaning and transforming raw data to make it suitable for analysis and modeling. Raw data often includes missing data, outliers, and other inconsistencies, such as formatting issues. Preprocessing steps include data cleaning, data normalization, and data transformation. The goal of data preprocessing is to improve both the accuracy and efficiency of downstream analysis and modeling.
MATLAB® provides apps and functions to preprocess input data to make it suitable for statistical modeling, machine learning algorithms, and other data-driven applications.
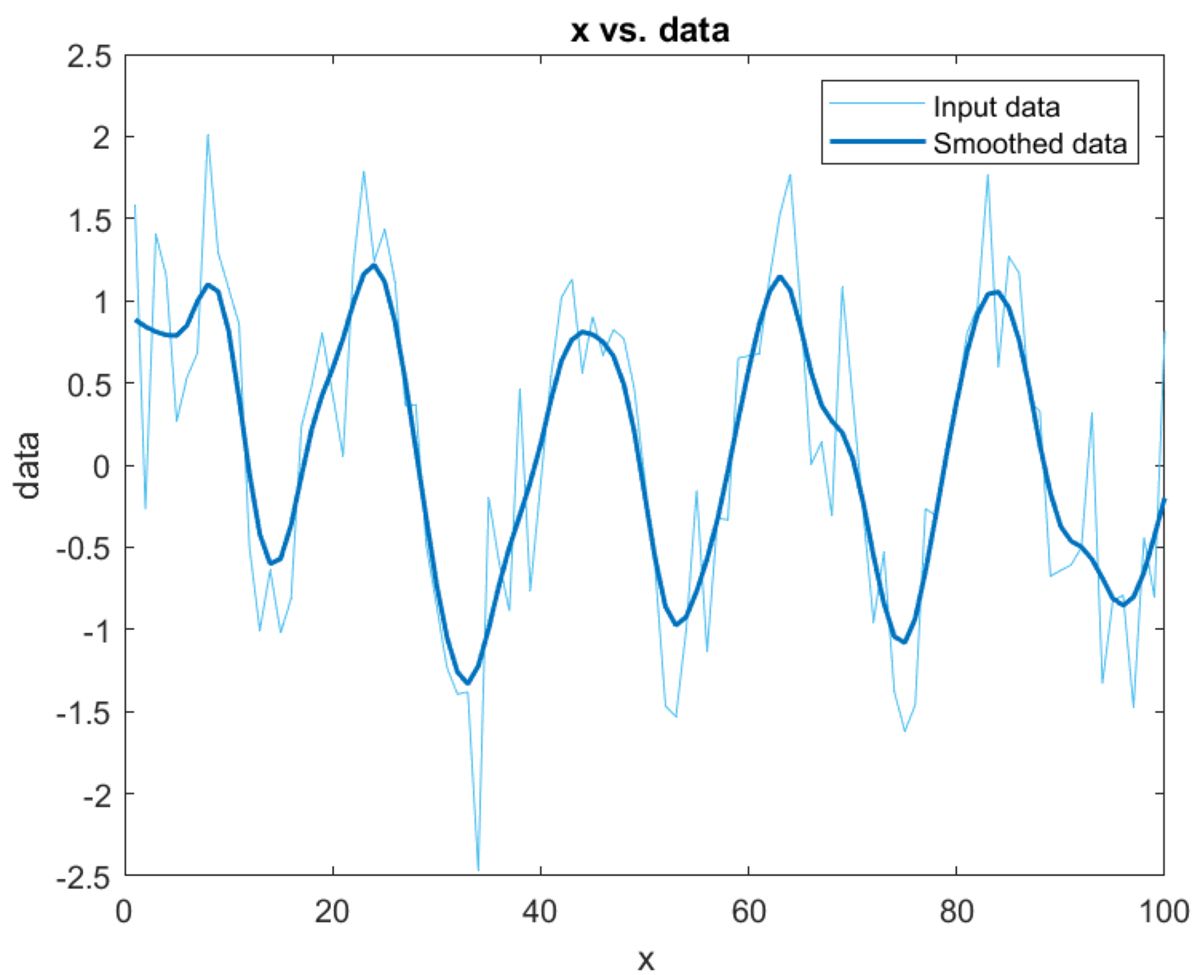
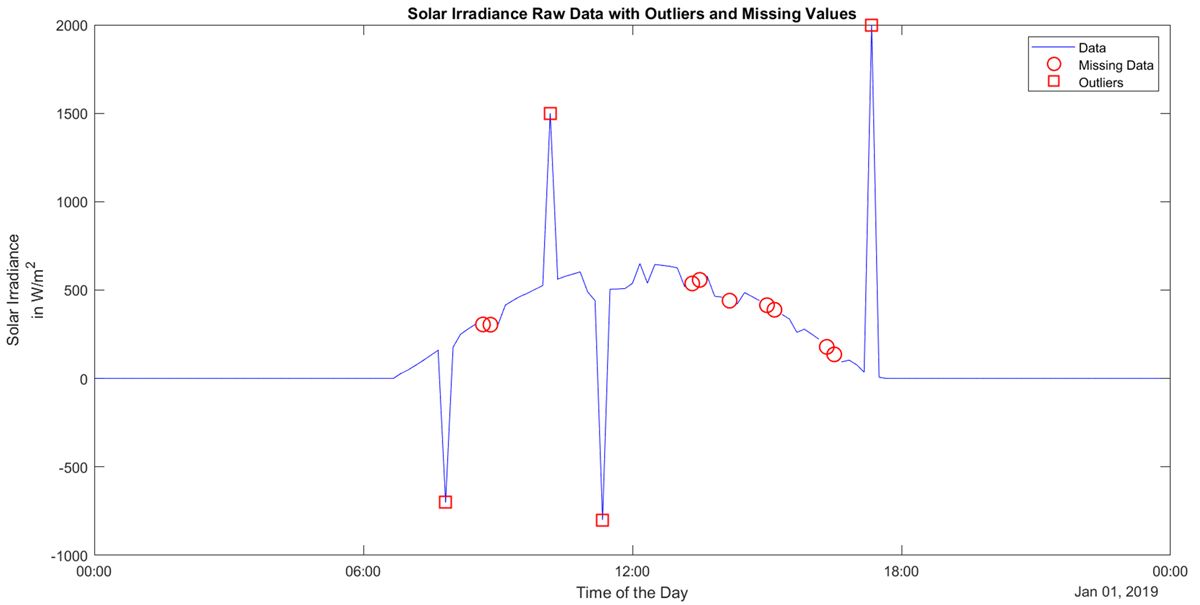
Figure 1 shows raw data that includes missing values and outliers, which can lead to erroneous conclusions during analysis. Figure 2 shows the same data after applying three different data preprocessing techniques—filling missing data, removing outliers, and smoothing. The improved data quality now prominently shows attributes such as magnitude, frequency, and nature of periodicity.
Data Preprocessing Techniques
Data preprocessing techniques can be grouped into three main categories: data cleaning, data transformation, and structural operations. These steps can happen in any order and iteratively.
Data Cleaning
Data cleaning is the process of addressing anomalies in the data set using techniques such as:
- Managing outliers: Identifying, and then removing outliers, or replacing them with statistically estimated values.
- Filling missing data: Identifying missing or invalid data points and replacing them with interpolated values.
- Smoothing: Filtering out noise using techniques such as moving mean, linear regression, and more specialized filtering methods.
Data Transformation
Data transformation is the process of modifying a data set into a preferred format by using operations such as:
- Normalization and rescaling: Standardizing data sets with different scales into a uniform scale
- Detrending: Removing polynomial trends to enhance visibility of variations in the data set
Structural Operations
Structural operations are often used for combining, reorganizing, and categorizing data sets and include:
- Joining: Combining two tables or timetables by rows using a common key variable
- Stacking and unstacking: Reshaping multidimensional arrays to consolidate or redistribute data within the table, making it easier for analysis
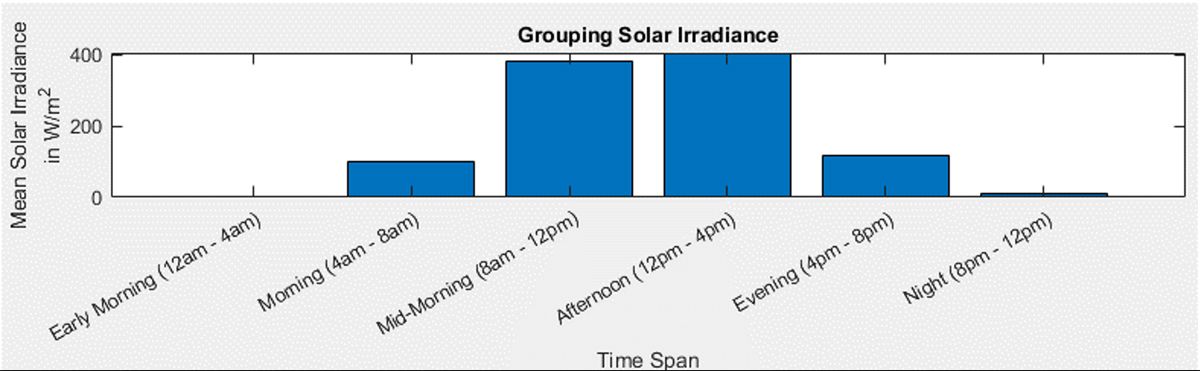
- Grouping and binning: Reorganizing the data set to extract valuable insights
- Calculating pivot tables: Breaking down large tabular data sets into sub-tables to gain focused information
Data Preprocessing and Data Types
Data preprocessing steps can be different depending on the type of data. Here are three examples of different data preprocessing methods, available for various data types.
| Time-Series Data | Tabular Data | Image Data |
| You can perform a variety of data cleaning and preprocessing tasks such as removing missing values, filtering, smoothing, and synchronizing timestamped data with different time steps. | When a table has messy data, you can clean the table by filling in or removing missing values and rearranging table rows and variables in a different order. | Data preprocessing is useful for applications involving images, including AI. You can preprocess your data by resizing or cropping the images, or even by increasing the amount of training data for deep learning models. |
|
|
|
| Preprocess and Explore Time-Stamped Data | Clean Messy and Missing Data in Tables | Preprocessing Images for Deep Learning |
Data Preprocessing with MATLAB
Choosing the right preprocessing approach is not always obvious. MATLAB provides both interactive capabilities (apps and Live Editor tasks) and high-level functions that make it easy to try different methods and determine which is right for your data. Iterating through different configurations and selecting the optimal settings will help you prepare your data for further analysis.
Interactive Capabilities
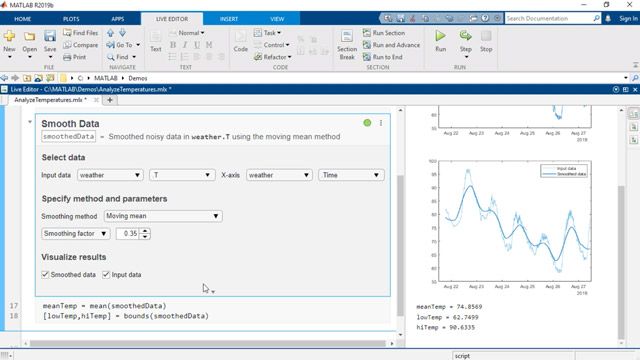
The Data Cleaner app is a standalone interactive tool for preprocessing time-series data without writing code. Figure 6 shows how to import your data and then clean it, fill in missing data, and remove outliers. You can then save your modified data to the MATLAB workspace for further analysis. You can also automatically generate MATLAB code to document your steps and reproduce them later.
Live Editor tasks are simple point-and-click interfaces that you can add directly to your script to perform a specific set of operations. These tasks can be configured interactively to iterate through different settings and identify the optimal configuration for your application. As with the Data Cleaner app, you can also automatically generate MATLAB code to reproduce your work.
You can interactively preprocess data using a sequence of Live Editor tasks such as Clean Missing Data, Clean Outlier Data, Normalize Data, etc., by visualizing the data at each step.
Using MATLAB Functions
MATLAB provides thousands of high-level, built-in functions for common mathematical, scientific, and engineering calculations, including data preprocessing.
You can start exploring your raw data set by visualizing it in MATLAB. Figure 9 shows raw data consisting of missing values and outliers. The data set captures the solar irradiance received on a typical day. Harsh weather conditions could interfere with wireless telemetry transmission resulting in a raw data set with imperfections.
Here are five common data preprocessing techniques applied to a raw solar irradiance data set shown in Figure 9 using MATLAB.
| Data Preprocessing Technique | MATLAB Plot |
|---|---|
Addressing Outliers: Anomalies in the telemetry data show up as outliers. The outliers are removed using |
|
Filling Missing Data: Loss of communication results in missing data in telemetry. Use |
|
Smoothing Data: Noisy solar irradiance data is removed using |
|
Normalize Data: Using the |
|
Grouping: Use |
Data can be messy, but data preprocessing techniques can help improve data quality and prepare your data for further analysis. See the resources below for more information.
Examples and How To
Software Reference
See also: data cleaning, MATLAB for data analysis, MATLAB graphics